Companies and organizations typically prioritize their branding efforts toward their target customers. This is because customers and consumers are crucial for the success of any business, and marketing strategies naturally revolve around them.
But what if we told you that branding has the power to attract a whole different set of stakeholders?
In this article, we’ll focus on using brand strategies to attract and retain employees and dive into the exciting world of employer branding.
It’s time to shift our perspective and discover how branding can work wonders in captivating top talent and building an engaged and motivated team.
50 Video Lessons | In-Depth Workbook | Templates | Support
The Ultimate Brand Building System is now open for registration. Enroll today to stand out in your market and create a future-proof brand!
Table of Contents
What does employer branding mean?
Kristin Backhaus and Surinder Tikoo conducted extensive academic research on employer branding. They provide the following definition:
“Employer branding represents a firm’s efforts to promote, both within and outside the firm, a clear view of what makes it different and desirable as an employer.”[1]
In other words, it is a facet of a brand strategy that focuses on managing prospective and current employees’ perceptions, reputation, and engagement.
As a brand, it is crucial to foster a positive employment experience and persuade individuals that the organization is an excellent workplace. This attracts top talent and ensures that current employees are satisfied and motivated in their roles.
The employer branding framework: key areas to consider
Academic researchers Backhaus and Tikoo have developed an Employer Branding Framework that visually summarizes how this concept can derive in employer attraction and employee productivity:[2]
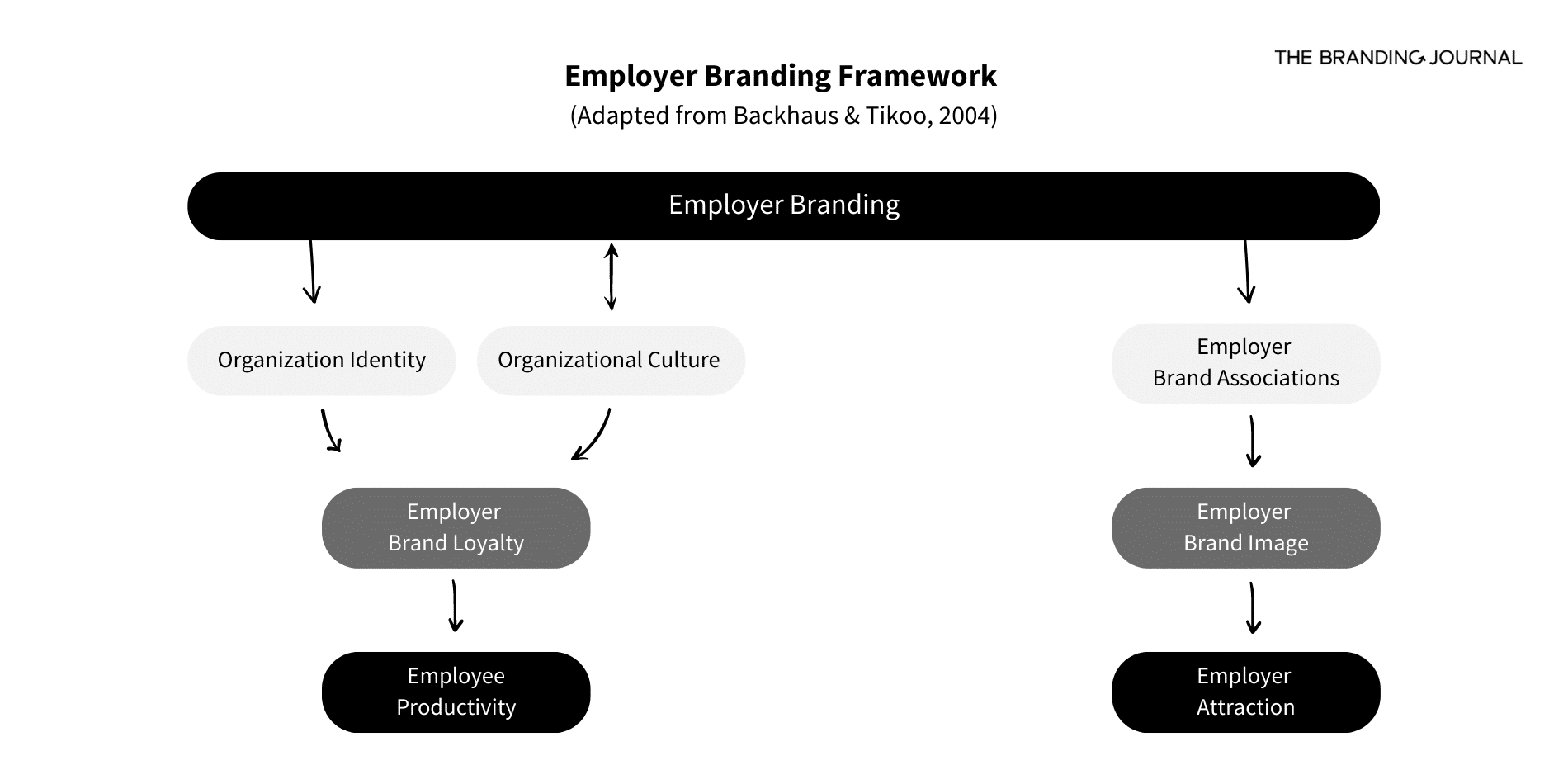
As shown in the graph, employer branding directly influences how potential candidates view and are attracted to a brand, as well as the loyalty and productivity of current employees.
According to the authors, this is mainly achieved by influencing three key aspects:
- Employer brand associations
Potential applicants identify with brands that share similar values, beliefs, and personalities. When there is a strong connection between these associations and the employer brand, people are likelier to want to work for the organization. Employer brand associations have a direct impact on the employer brand image and the employer attraction. - Organizational identity
Organizational identity refers to the collective image that members of the organization hold about it. This image should be appealing and unique. Individuals who strongly identify with the organization’s identity become more committed and dedicated. - Organizational culture
The organizational culture should create a desire to work for the brand and support employees’ professional well-being. A positive and engaging culture makes the employer brand more attractive and improves employees’ satisfaction.
What are the benefits of employer branding?
Investing time and effort into an employer branding strategy provides numerous benefits to the organization:
1. Attracting qualified talent
By fostering motivation to work for the brand, employer branding helps attract qualified talent.
2. Increasing employee satisfaction and retention
Employer branding contributes to a positive work environment, reducing turnover and increasing employee satisfaction and retention.
3. Boosting employee motivation and productivity
Employer branding initiatives boost employee motivation and productivity, leading to higher levels of performance, innovation, and overall organizational success.
4. Gaining a competitive advantage
Employer branding gives companies a competitive edge when seeking employees with similar skills and experience.
5. Safeguarding the brand’s image
Employer branding safeguards the brand’s image in the minds of current and potential employees, who may also be customers.
6. Reducing costs
Investing in employer branding reduces costs associated with attracting new applicants (such as job advertising and third-party recruiter expenses) as well as costs associated with unfilled positions and staff training.
7. Improved brand image and customer loyalty
The way a company treats its employees and the experience candidates have when applying for jobs can significantly affect the image these people have about the overall brand and its products. When candidates have a bad experience during the hiring process, they will likely stop buying from that company.
Moreover, a study by CareerArc found that 64% of people have stopped buying from a brand after hearing about how poorly its employees are treated.
8. Enhanced organizational performance
Overall, it is essential to recognize that attracting and retaining the right talent is essential for enhancing organizational performance. Investing in human resources is a key factor in achieving success, and employer branding can play a significant role in supporting this objective.
What is the connection between the employer brand, the product brand, and the corporate brand?
The employer brand is closely connected to the product/corporate brand – with a different objective: appealing to employees instead of customers.
Both the employer brand and the product brand mutually influence each other. Altogether, they impact the corporate/organization’s overall brand (awareness, image, and reputation).
In the following graph, adapted from a research paper by the Lancaster University Management School[3], you’ll see the interconnection between these three concepts.
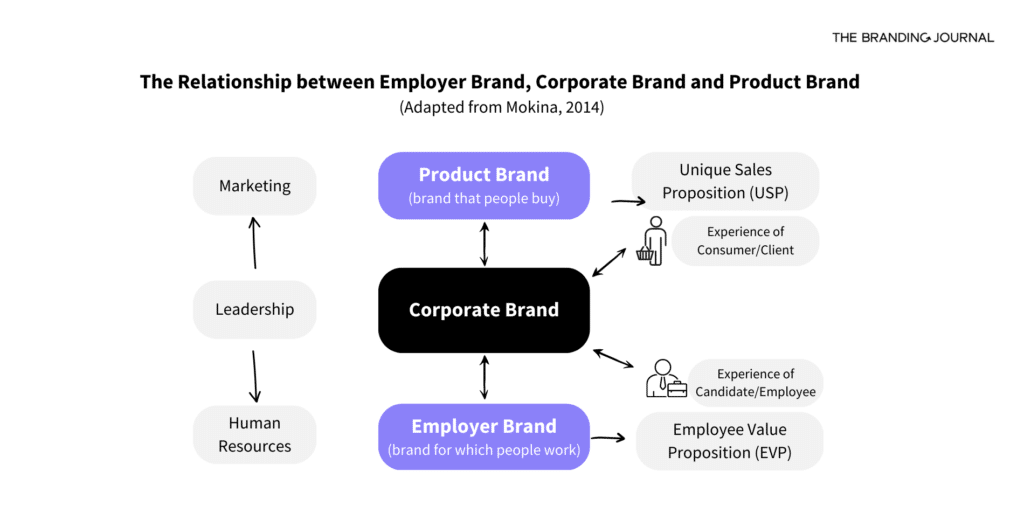
Here are some key points to consider:
Different objectives:
- The employer brand focuses on how the organization is perceived as a workplace.
- The product brand focuses on how target customers perceive the organization’s products and services.
- The corporate (or organizational) brand focuses on how the organization is perceived as a whole. It’s how people feel and think when exposed to the organization’s name.
Interconnection:
These types of brands can influence each other positively or negatively.
- Examples of positive influence:
– If a company has a strong employer brand, it can attract and keep skilled employees who can then play a crucial role in implementing the product or corporate brand strategy.
– When a company has a strong product or corporate brand, it can create a positive impression of the organization as a whole, making it more attractive as an employer.
- Examples of negative influence:
– If people have a bad experience during the hiring process or at work, it can make them think negatively about the organization as a whole, both as a workplace and in terms of its products.
– If people negatively perceive the brand and its products, they may be less inclined to apply for job opportunities within the organization.
It’s crucial to recognize that many companies primarily concentrate on their product brand, often overlooking the development of a comprehensive corporate brand strategy. The product brand, which is designed to appeal to target customers, typically becomes the focal point of most organizations’ single-brand strategy. In fact, when we talk about brand strategies, we often talk about what we call the product brand.
In many cases, especially in smaller companies or those with a single primary product or service, the product, and corporate brands may be considered the same internally and externally. This is because the company’s identity is strongly tied to its product or service.
In any case, it will be important to ensure that the employer brand matches the overall branding efforts of the company, including its products and corporate image. If the overarching brand embodies a specific purpose, values, mission, and vision, these elements should be mirrored in the employer brand.
Consistency and harmony across all branding efforts are vital in maintaining a robust brand presence.
Key Takeaways
- Employer branding is a firm’s strategy to showcase its unique and appealing qualities as an employer, managing the perceptions and engagement of potential and current employees.
- The benefits of employer branding include attracting talent, gaining competitive advantage, protecting brand image, reducing recruitment costs, and enhancing employee satisfaction, retention, and productivity.
- The employer brand and the product brand are distinct but interconnected, influencing each other and impacting the organization’s overall brand and reputation.